What is neuropathy?
What exactly is neuropathy?
Neuropathy is a chronic, progressive, and often disabling condition that affects nerve cells. It is the result of many things that leads to the condition called neuropathy. We will cover more causes later on this page but a shortlist for now would include peripheral neuropathy caused by diabetes, infection, mechanical injuries, vascular and autoimmune disorders, and post-infectious conditions. Neuropathy means numbness or weakness in the peripheral nerves.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there are approximately 1 billion people with neuropathy worldwide. That is a staggering number. And the majority of those would fall into the peripheral neuropathy category.
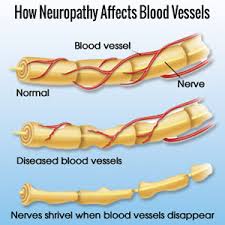
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy & Other General Neuropathy -Peripheral Nervous Sytem
Each nerve of our peripheral nervous system has specific functions, and symptoms vary depending on how they affect us. Generally speaking, the signs of peripheral neuropathy could be mistaken for other ailments. Peripheral neuropathy is caused by a nerve that is located in a single nerve (mononeuropathy) or two or more nerves in multiple locations. Carpal tunnel syndromes represent mononeuropathy. People suffering from peripheral neuropathies typically experience polyneuropathies. Poly means many.
The neuropathy symptoms depend on which nerves are affected. In the UK it’s estimated almost 1 in 10 people aged 55 or over are affected by peripheral neuropathy and suffer challenging neuropathy symptoms.
Brain and Spinal Cord -Sensory Nerves
The peripheral nervous system is the network of nerves that lie outside the brain and spinal cord). It includes different types of nerves with their own specific functions, including sensory nerves – responsible for transmitting sensations, such as pain and touch motor nerves – responsible for controlling muscles autonomic nerves – responsible for regulating automatic functions of the body.
This is why when the motor nerves affected don’t send the autonomic nerves the message fast enough then people with neurological disorders often stumble and fall. Diabetic neuropathy patients often get injured by hitting an object but not knowing they’ve done it and the damaged peripheral nerves don’t send the pain signals to the brain and spinal cord so they sustain a physical injury. As stated, it happens a lot with diabetic neuropathy and is one of several symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. The
In fact, peripheral neuropathy describes so many affected nerves, especially when it is chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy, that there is a peripheral neuropathy fact sheet. According to the NIH, over 20 million people in the USA have peripheral neuropathy. To learn more you can read about it on the peripheral neuropathy fact sheet found here.
Included below is a list of common symptoms of neuropathy:
Chronic neuropathic pain
Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Facial numbness
Dizziness and vertigo
Limited use of limbs due to pain or paresthesias
Severe pain in multiple locations
Tingling and/or burning sensations in the legs
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Painful numbness
Nausea
Fatigue
Headaches
Dizziness
Anxiety
Complications of Neuropathy
The complications of neuropathy are caused by loss of sensations from further nerve damage. The reason for neuropathy is not usually the initial injury but it can be a minor blister in new footwear.
The resultant infections are much more common among people with diabetes. When feet feel less sensation they may develop areas of increased pressure causing sores or ulcers. It is often necessary that the amputations be carried out when an ulcer develops.
How is peripheral neuropathy diagnosed?
Neuropathological symptoms can be confusing and can result in confusion. The diagnosis of neuropathy usually entails additional diagnostic testing is usually required for a diagnosis of the cause.
Test of neuromuscular function Neuropathological test of nerve appearance Autonomic test. Ultrasonographic examination of the muscle tissue can identify the muscle imbalances associated with muscle problems or injuries.
Muscle weakness and muscle and nerve ultrasound
The diagnosis can be made using various means, he said. Usually, this process involves having your doctor make up your patient’s history and examining the affected region for an assessment of its function. After this time, the testing could take place.
There are an estimated 200 million people worldwide who suffer from some form of neuropathy. Each year, 5-10% of new cases are diagnosed with neuropathy, which is often associated with diabetes but can also occur independently.
One theory behind neuropathy is that disease damages peripheral nerves; another theory is that nerve damage causes symptoms as a result of damage to other organs such as the heart or kidneys.
There are signs and symptoms which are similar between patients with diabetes and neuropathy — so it’s important to check both when evaluating each case. It’s also important to remember that neuropathic pain can be present at any time — so it’s not necessarily related to diabetes alone! It is estimated that there will be an increase in diabetic foot ulceration by 2030 due to lower quality care, rising rates of infection, poor hygiene practices / poor foot care habits among diabetics as well as other lifestyle factors (like smoking).
So it’s important for diabetics to maintain good hygiene habits, especially in order for their feet to heal properly. If you suspect your diabetic foot has ulcerated, seek medical attention immediately. If you have any doubts about your diagnosis please seek medical attention at once. You can also search for “diabetes nerve pain treatment” on Google.
On this page, there are links regarding ulcerating diabetic feet from around the world. If you have questions about how much insulin you should take, please read this page. For more information on treating ulcers please read this page.
For more information on how insulin works please read here. For more information about diabetic foot ulcers please read here!
What is the main cause of neuropathy?
While most people think of diabetes as the main cause of neuropathy, it is not. There are many other reasons why people develop this condition.
Peripheral neuropathy results from one common cause of diabetes. The pain of patients with peripheral neuropathies can typically be felt by feeling tingling or stumbling.
Neuropathy is a group of conditions that affect nerves and causes pain. There are three main types: peripheral neuropathy, deep neuropathy, and central neuropathy.
We should look at three major factors to understand what causes this condition:
Age
Genetics (heredity)
Environmental factors (e.g., smoking, lack of exercise)
Diabetes
Stroke and heart attack
The flu/cold/bronchitis/pneumonia
Cancer
Surgery (usually involving the foot)
Vitamin deficiencies
Chemotherapy
Nerve fibers damages
Nerve tissue damage
Immune system issues
trauma
infection
metabolism issues
inhaling toxins
physical exposure to toxic substances
Nerve compression
In addition to diabetes and other metabolic disorders, we should also consider what kinds of exercise people do or don’t engage in while they are living with a diagnosis that will impact the symptoms of neuropathy.
All these factors come into play when you’re looking at who is affected by this debilitating condition and how they need to be managed by a doctor in the long term future.
Peripheral neuropathy risk factors include Diabetes, especially if your sugar levels are poorly controlled Alcohol misuse, Vitamin deficiencies, particularly B vitamins Infections, such as Lyme disease, shingles, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B and C, and HIV, digestive and kidney diseases Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus and other autoimmune diseases.

Is neuropathy curable or reversable?
Neuropathy is a term used to describe the damage that can occur to nerves and the brain (but not the spinal cord) due to diabetes or other diseases (such as stroke). It can be described as an inflammation of nerves, which may or may not result in pain.
As there are so many causes of neuropathy, it is hard to know what exactly neuropathy is. Risk factors include kidney disease, heart disease, infections, and even some medications like corticosteroids.
Some forms of neuropathy can be reversed by treatment. If untreated, cases will become chronic and slowly get worse over time. There is not a cure known for neuropathy. There are three kinds of neuropathy:
The first type is called post-traumatic neuropathy which happens when nerve tissue has been damaged during a serious injury or surgery such as a stroke. This type of neuropathy can be treated with medication and surgery though it typically responds only to very specific treatments such as nerve stimulation therapy (NST).
The second type of post-traumatic neuropathy is called primary post-traumatic neuropathy which happens before there have been any major injuries or surgeries. This type cannot be treated with medications and surgery but has been linked with certain types of chemotherapy drugs called neoadjuvant chemotherapy which help reduce the amount of damage caused by cancer treatments.
A third form sometimes occurs in people who have had diabetes for a long time, called “atypical” post-traumatic neuropathy which usually happens after more severe diabetic complications like diabetic retinopathy (diabetic eye disease) or peripheral arterial disease (blood vessel blockage).
These people often do not respond well to NST therapy though they can sometimes benefit from other medical treatments such as anti-Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and blood pressure drugs called angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for sensory nerves and nerve function may have modest success in some cases.
Sometimes people with atypical post-traumatic neuropathies respond better to surgical procedures called patching where pieces of damaged nerves are surgically removed instead of being cut away completely.
Most physicians don’t understand why this happens so they don’t know how best to treat it, so they just tinker with different methods while trying to find out what works best for them.
They use many different tests such as nerve conduction studies, pharmacokinetic studies, electrophysiology studies, ultrastructural studies, acidity studies, etc., etc., all in hopes that they will figure out some way that they can treat
Duration of Neuropathy
Neuropathy can last a lifetime, or become permanent. Nevertheless, nerve damage in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy will only last a short time. One-third of chemotherapy-treated patients experience neuropathy after one month of treatment. By six months of age, this percentage was down to 30 percent.
What is peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is often caused by damage to nerves that reside outside the brain or spinal cord, essentially meaning on the periphery and that is why it is called peripheral neuropathy, effecting the peripheral nerves. It has an impact on other body processes and processes, including digestive digestion. Your peripheral nervous system transmits information from your brain and spine into your whole body. In addition, the peripheral nerve transmits sensory data to the central nervous system. Peripherals Neuropathy is caused by traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic disorders, acquired diseases, inherited, or exposures to toxic substances, nerve compression, and other conditions. Diabetes has a very high prevalence.
Peripheral neuropathy involves a condition affecting peripheral nerves. These nerves send messages from one nerve system to another. Peripheral neuropathy is a term used to describe various disorders due to damage to the peripheral nervous system that communicates with the central nervous system. In some instances, the nervous tissue can determine whether your hands feel cool or not if you have touched your hand. Peripheral neuropathy has reshaped the lives and health of 20 million Americans who trust sources for information. The condition usually leads to lost nerve signals or distorted signals causing improper signals like when there are symptoms of sensory neuropathy.
Tell me more about nerve damage
Symptoms depend on the nerve types affected. Generally, motor nerve damage occurs as a result of muscle weakness. Other symptoms are painful muscle contractions or fasciculations. Sensory neurodegenerative disorders cause many symptoms. Sensorially sensitive neuron is an essential component of many functions. Autonomic nerve damage affects the axon of small fiber neuropathy. Common symptoms include excessive sweating and cold intolerant inability to expand small blood vessels, controlling blood pressure, and digestive symptoms.
How are peripheral neuropathies classified?
More than 100 different types were identified with different symptoms and prognoses. Symptoms differ according to the type of nerve damage – motor, sensory or autonomous. Neuropathy affects the third type of nerve fiber at different varying rates. The doctor uses terms like predominantly motor neuropathy, predominant sensor neuropathy, or neuromotor neuropathy as a description of different symptoms. The longest nerve ends of the foot are often where symptoms are first or worsened.
Prevention of Neuropathy
According to the Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy, you can adjust the diet of the person whose neuropathy occurs; The causes can include a lack of vitamin B12. (411 – 393) In addition, exercising can prevent and slow diabetic nerve damage. Nevertheless, neuropathy may have a hereditary cause. The illness is caused by weakness and atrophy of muscle tissue and affects millions of Americans.
Exercise and neuropathy
Having fitness in your routine will decrease muscle tension and reduce pain. In diabetics, regular physical activity lowers blood cholesterol (hyperglycemia). But be sure to contact your healthcare team prior to exercising since neuropathy can impact your ability to react to injuries.
Diabetic Neuropathy Further Nerve Damage and Neurological Disorders?
Nerve damage can be caused by a variety of things including diabetes and chemotherapy. Neuropathy or peripheral neuropathy is not just any health condition that is defined but is merely one term that describes various health problems that involve damage to peripheral nervous systems. While reversible, neuropathy can be treated through eating, lifestyle, and treatments that may or may not include medication.
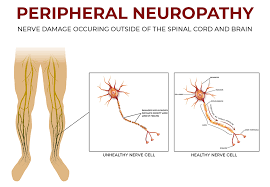
Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathology may occur when neural connections to the central nervous system are altered and disrupted. The nerve fibers send the pain signals to let us know there is an issue. But the numb pain experienced with this progressive degenerative
What are the three categories of neuropathy?
Which type of neuropathy is yours? Mononeurolopathy: A neuropathy causes nerve damage that affects only one nerve. ( Polyneuropathy – A common condition causing multiple nerve injuries can be treated as polyneuropathy. It depends on whether there is an autonomic sensory nerve or a combination thereof. Autonomic nerve damage can alter the functioning of the blood pressure of the individual.
The nervous system the brain and overall nerve health are resilient and respond in many cases to proper nutrition, proper treatments, and the proper consistency by the patient.
